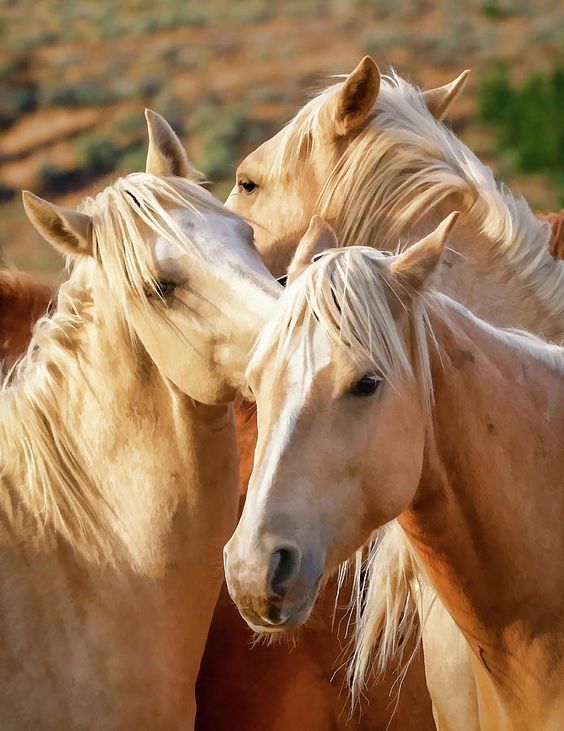
One of the keys to working safely together with your horse is knowing its pure conduct. If you’ll be able to predict when a horse will present aggression or concern of one thing, you’ll be able to react sooner and higher, keep away from a harmful state of affairs or forestall it from occurring. The article beneath explains the fundamentals of pure horse conduct.
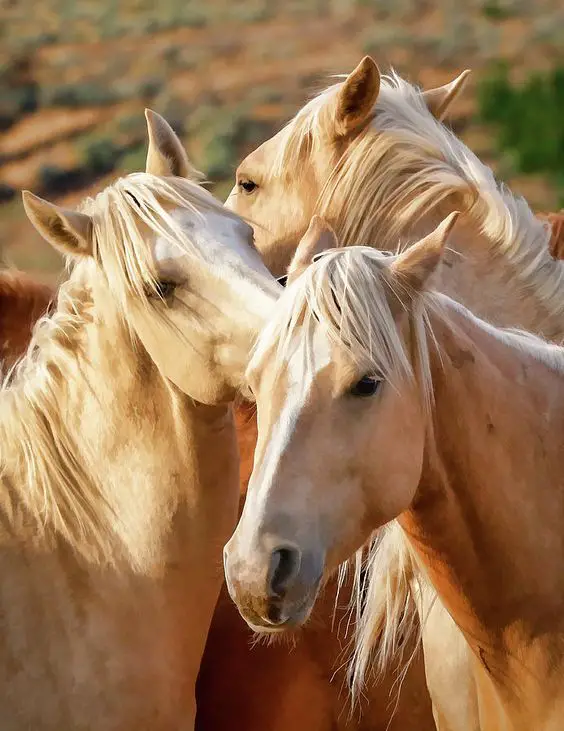

To start with, I wish to give ten theses concerning the survival of the horse within the wild.
- A horse is a sufferer animal. Its survival in its pure atmosphere will depend on its flight intuition. Natural enemies that pose a risk to the horse are predators, so its capacity to outrun them is crucial. To totally perceive the character of horses, we should perceive the character of their flight intuition.
- Horses are among the many most attentive and cautious of all home animals. Since they’re prey in nature, horses should be capable to detect predators. A stimulus unnoticed by people typically causes nervousness in horses (as riders and trainers, we normally mistake this response for “fright” or unhealthy conduct).
- The horse has a really quick response time. The prey animal should instantly react to the alleged predator – that is the one approach it may possibly survive.
- Horses could be desensitized to intimidating stimuli. They can rapidly be taught what’s harmful (lion, puma, and so on.) and what’s innocent (birds, rocks, and so on.), so that they don’t spend their total lives operating away from each object.
- Horses forgive, however don’t neglect. They bear in mind unhealthy conditions particularly nicely! This is why it is vitally essential to make the horse’s first coaching expertise optimistic.
- Horses categorize their experiences in mainly considered one of two methods: a) one thing is just not scary, could be ignored or explored, and b) one thing is frightening, it’s essential to run. Therefore, while you introduce one thing new to a horse, you should do it in order that it chooses possibility “A”. Again, it’s essential to make your entire coaching expertise a optimistic one.
- Horses are pretty straightforward to dominate. A horse is a herd animal, and a hierarchy is all the time established in herds. If accomplished accurately, an individual can simply change into a pacesetter for a horse, dominate throughout coaching, with out inflicting extreme concern in it.
- Horses dominate, controlling the motion of their neighbors within the herd. They fall underneath domination when: a) we or one other animal makes them transfer when they don’t wish to, and b) we or one other animal intrude with their motion once they wish to run (examples – utilizing a barrel, wire circle; in a herd – extra dominant horse pursues much less dominant).
- Horse physique language is exclusive. As a extremely social animal, the horse communicates its feelings and intentions to its mates via each vocal cues and physique language. The individual answerable for the horse should be capable to learn the horse’s physique language in an effort to change into an efficient coach.
- Newborn foals are neurologically mature. They are most weak instantly after start, so they have to be capable to determine hazard and flee if essential.
Social Structure
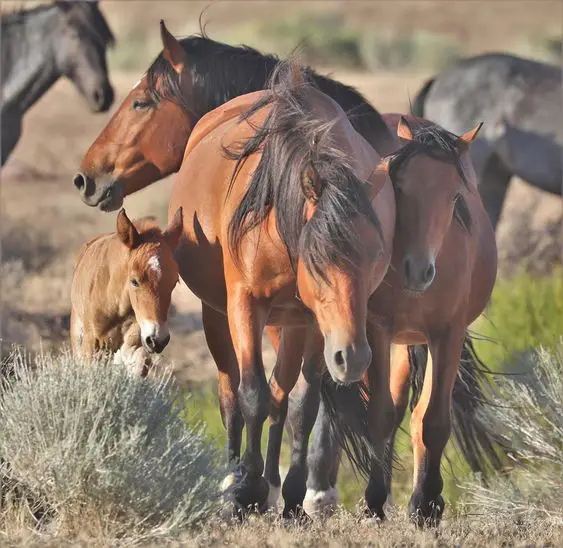

A herd of untamed horses consists of 1 or two stallions, a bunch of mares, and their foals. The chief of the herd is normally the previous mare (“alpha mare”), even when there’s a stallion within the herd. She retains her dominant position, though she could also be bodily weaker than different horses. The older mare has extra expertise, extra contact, and has skilled extra threats than every other horse within the herd. The requirement for a number one horse is just not energy or dimension; if that had been the case, then people may by no means dominate horses. Dominance is predicated not solely on aggression but in addition on a relationship that permits one horse to know that one other horse expects them to obey.
The activity of the stallion is to be the keeper and protector of the herd, in addition to to keep up reproductive vitality. A stallion’s harem normally consists of 2-21 horses, as much as 8 of that are mares, and the remaining are their descendants. When the foals are sufficiently old to take care of themselves, they kind a herd of bachelors. The mares both keep of their herd, or (most frequently) go to a different, or kind a brand new herd with a bachelor stallion.
As quickly as a stallion turns into too previous to keep up its standing as a herd grasp, he’s changed by a youthful stallion from the bachelor herd. The common lead time of a stallion is about 2 years, however some might stay leaders for greater than 10 years.
Horses are most weak once they eat or drink. Therefore, when the horse is submissive, it would feign meals by decreasing its head, chewing on its jaw, and licking its lips.
Dominance is characterised by the flexibility of 1 horse to make one other transfer in opposition to its will. The horse will push the opposite or make it run away with out contact. If the horse doesn’t transfer or reacts aggressively, the dominant horse will combat to substantiate or problem his standing.
Feelings
The horse’s imaginative and prescient is the first hazard detector. Despite having poor coloration imaginative and prescient, horses can distinguish blue and crimson from grey shades. Horses, nonetheless, have extra issues distinguishing between yellow and inexperienced from grey. Horses even have poor depth notion when utilizing just one eye. They can’t inform a trailer from an limitless tunnel or a puddle from a bottomless lagoon. Their notion is improved by about 5 occasions when utilizing each eyes (binocular imaginative and prescient). They can immediately change focus from close to to distant objects. This is why horses transfer their heads to completely different positions to see close to and much objects.
Horses have a eager capacity to detect motion. This is why horses are extra fearful on windy days; objects that had been normally stationary now transfer and are perceived by them as a possible risk.
Horses see nicely at night time, however their sensitivity is lower than that of cats.
The mechanics of a horse’s imaginative and prescient are completely different from ours. They can see virtually panoramic, with a small blind spot within the entrance, in entrance of the muzzle, and behind, behind the tail.
Never strategy the horse silently from the back and front. If you scare a horse by out of the blue rising from the blind spot, it may possibly use considered one of its protection mechanisms – hitting you or operating away.
A horse can see two issues without delay, one with every eye. This is feasible as a consequence of the truth that every a part of her mind can work individually. Like people, horses have a dominant aspect (proper or left); nonetheless, in contrast to people, horses want to check the topic twice: on the correct aspect and on the left.
The expression of a horse’s eyes is usually thought-about to be a superb reflection of her psychological state (for instance, wide-open eyes when a white physique is seen signifies concern, half-closed eyes point out sleepiness and rest, and so on.).
The horse’s listening to is way sharper than ours. Horses use their listening to to detect sounds, find an object making a sound, and obtain sensory info that permits the horse to acknowledge the character of the sound supply. Horses can hear sounds at low and really excessive frequencies within the vary 14 Hz to 25 okHz (human listening to vary 20 Hz to twenty okHz). Horse ears could be rotated 180 levels utilizing 10 completely different muscle tissue (the human ear can solely transfer thanks to 3) and are in a position to spotlight a particular space that must be listened to. This permits the horse to navigate the sounds to find out what’s making a noise.
Horses are extraordinarily delicate to tactile sensations or contact. Their entire physique is as delicate as our fingertips. They can really feel each a fly that has settled on one hair and any motion of the rider.
Body Signals

Horses are superb at letting us know the way they really feel; the one downside is that most individuals don’t perceive their “language”. We gives you some ideas. So:
If the tail of a horse:
- Raised excessive – she is alert or excited.
- Dropping low is an indication of exhaustion, concern, ache, or submission.
- Located on the highest, virtually on the again (as most foals do) – a playful temper or the horse may be very anxious.
- The horse is tailing – it’s irritated.
Let’s transfer on to the legs. If:
- The horse is digging – it’s upset.
- One entrance leg raised – the horse might present a mild risk (this may increasingly typically be a traditional feeding stance).
- The leg is raised – that is typically a extra pronounced risk.
- The horse stomps – this means a gentle risk or protest (maybe that is how the horse is making an attempt to do away with bugs or flies that chew its legs).
Facial expression:
- Sucking motion – This is how foals typically present their submission to older horses. They open their mouths, pull the corners of the lips again, then open and shut their jaws.
- The jaws are open, the tooth are bared – the horse is displaying aggression or is able to assault.
- Flehmen. This reflex is triggered by intense or uncommon odors. Usually, stallions present it once they sense the mare within the hunt. They suck in air and elevate the higher lip up and again.
- Dilated nostrils are normally an indication that the horse is agitated or alert.
- The whites of the eyes are seen – normally means the horse is offended or scared. (Protein is seen within the Appaloosa horses and is a traditional attribute.)
Horse ears are a singular indicator:
- Neutral place – ears are directed freely upward, auricles are directed ahead or outward.
- The horse’s ears are turned ahead, directed upward. This signifies that one thing has caught the horse’s consideration.
- The ears are set aside just like the wings of an airplane. This normally means the horse is drained or depressed.
- Drooping ears (ears drooping down and to the aspect) normally point out fatigue or ache.
- Ears turned again (the auricles are directed again in the direction of the rider) – normally means attentiveness to the rider, the horse listens to the command.
- Blocked ears – The horse is offended and aggressive.
Communications:
Horses have a wide range of modes of voice and non-voice communication. Voices embrace a yelp or scream, which normally signifies a risk to a different horse.
Low and quiet sounds. The stallion makes such sounds when caring for the mare; the mare and foal make these sounds to one another; the horse makes this sound when it is aware of it is going to be consuming time quickly. Whinnying in excessive tones are sounds that may journey an extended distance.
The horse neighs so different horses know the place it’s when it tries to search out the herd. Horses additionally use neighing to speak to one another, even when out of the road of sight of one another.
Snoring, loud snorting, is a powerful, speedy expulsion of air via the nostril, leading to a loud sound that’s normally an alarm and is utilized by horses to alert others to hazard.
Quiet loud night breathing is a extra passive, shorter, and decrease model of loud night breathing, normally the results of one thing or mud entering into the horse’s nostril.
In the herd, together with alerts of aggression, there are additionally alerts of friendship. Mares and foals push one another whereas feeding, horses scratch one another’s manes and withers.
Vices:
Vices are damaging actions that happen for a wide range of causes, together with stress, boredom, concern, extra power, and nervousness. Horses of their pure atmosphere graze 12-16 hours a day. When retaining stalls, we don’t permit them to do what they do in nature – transfer across the pasture, talk with different horses.
Lack of pure stimuli forces the horse to invent his personal stimuli. Once these habits develop, they change into troublesome to remove.
Bite – the horse rests its tooth on a set floor (for instance, the sting of a stall door, a feeder, a fence), bends its neck, and sucks in air, making a attribute sound. This ends in the discharge of endorphins, which relieves the horse of stress. The chew turns into a behavior. Even when the stress or disagreeable state of affairs passes, the horse continues to chew at occasions. Some horses even favor biting over meals! Biting can result in weight reduction, poor efficiency, colic, and extreme tooth put on.
Pitching – the horse stands on the door of the stall and rhythmically strikes its weight from one entrance leg to the opposite, swinging its head. This could be brought on by boredom or extra power and may result in weight reduction, poor efficiency, and weakened tendons.
Hitting the partitions of the stall, wandering across the stall, digging, and making an attempt to chew the door of the stall are additionally vices brought on by boredom from being indoors. To cut back the frequency of this conduct, you’ll be able to strive including one other meal, inserting toys within the stall, offering the horse with extra roughage, and beginning out in a levada.
Horses gnaw on the picket components of the stall, eat bedding (not straw), their excrement, and in addition get satisfaction. These defects are brought on by lack of train or boredom. Improper vitamin can be the trigger. Add extra roughage to the horse’s weight-reduction plan, place salt and minerals within the stall. This can cut back the incidence of the defect.