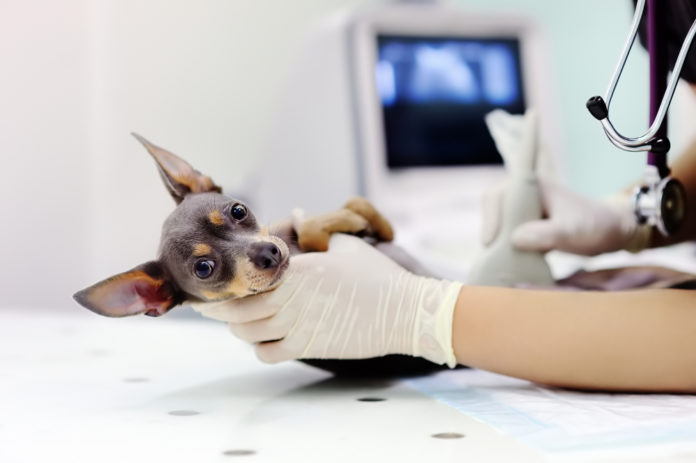
From CT scans to ultrasounds, there are a number of methods to see inside your canine or cat’s physique. Here’s how these diagnostic imaging strategies differ, and the professionals and cons of every.
Along with lab work reminiscent of blood and urine testing, your canine or cat might typically require diagnostic imaging research to have a look at the deeper tissues of his physique. Depending on his situation and the suspected downside, diagnostic imaging can embrace radiography, ultrasonography, a CT scan, and/or MRI scan. This article examines every of those modalities together with their execs and cons.
1. Radiography
This type of diagnostic imaging makes use of radiation to supply power (x-rays) that penetrate the physique to indicate underlying buildings reminiscent of bones and mushy tissues (organs). It is a typical imaging modality and is accessible in most veterinary hospitals. Radiography is among the “normal” exams I typically use to help me in making a prognosis and formulating a therapy plan.
Pros
- Inexpensive in comparison with different imaging strategies (usually underneath $500).
- Easily carried out.
- Allows for fast imaging.
- Often offers a prognosis for a lot of ailments (fractures, coronary heart failure, bladder stones, some sorts of most cancers, and so on.).
- Minimal ranges of radiation publicity.
Cons
- Uses ionizing radiation. While usually secure, the extra radiographs a canine or cat receives over his lifetime, the higher the chance of negative effects, reminiscent of most cancers. Also, there’s a lifetime radiation publicity stage that shouldn’t be breached; nonetheless, it’s unlikely this stage would ever be carefully approached until the animal receives massive quantities of radiation for most cancers therapy.
- May not reveal each downside (e.g. mind tumors, prolapsed spinal disks, and so on.), necessitating the necessity for various imaging modalities.
- Most animals should be sedated to attenuate the variety of radiographs and permit excellent positioning, and to attenuate radiation publicity to veterinary workers.
2. Ultrasonography/echocardiography
Ultrasonography is a well-liked diagnostic imaging device that appears inside your canine or cat’s physique by way of the usage of sound waves. Ultrasound examinations are most helpful for diagnosing circumstances that may very well be missed or not simply outlined utilizing a typical x-ray examination. This can embrace bladder stones, tumors of stomach organs, and free stomach fluid (as within the case of a bleeding tumor).
Echocardiography is an ultrasound examination of the center. It is often used to search for heart-based tumors reminiscent of hemangiosarcomas and, extra typically, for analyzing the center in an animal suspected of cardiac illness. While radiography can present coronary heart and blood vessel enlargement (a snapshot of the center and vessels), echocardiography exhibits the center and its elements (valves) in movement (i.e. a movement image of coronary heart muscle motion and blood movement). In my opinion, with extraordinarily uncommon exceptions, no canine or cat must be positioned on cardiac drugs with out echocardiography getting used to make a prognosis (see beneath).
Pros
- Inexpensive in comparison with different imaging modalities (usually underneath $600).
- Like radiography, it’s simply carried out, permits for fast imaging, and sometimes supplies a prognosis for a lot of ailments (coronary heart failure, bladder stones, some sorts of most cancers, and so on.).
- Uses secure sound waves.
- Most animals don’t should be sedated.
Cons
- May not reveal each prognosis, particularly very small tumors, necessitating the necessity for various imaging modalities.
- Sedation could also be wanted for fractious animals.
- Echocardiography gained’t reveal pulmonary edema (fluid within the lungs), which can require separate testing reminiscent of radiology.
3. CT scan
Computerized tomography (CT scan) makes use of x-rays to create the picture. However, as an alternative of utilizing a single x-ray, as in a typical radiograph, CT scans mix quite a few x-rays taken from totally different positions, and use superior pc know-how to create extra detailed photographs of the affected person. It’s simpler to see extra element of a physique half when it’s considered from a number of angles. Think of the distinction between a 2D picture and a 3D picture, and also you’re heading in the right direction. CT scans decide up lots of the similar issues as easy x-rays do, however in a extra detailed and exact method, making them notably helpful for detecting small tumors and inner bleeding.
Pros
- Often offers a prognosis for a lot of ailments not simply visualized by conventional radiography or ultrasonography.
Cons
- More costly in comparison with different modalities (usually $1,500 to $2,500).
- Requires referral to a specialty middle.
- Scan takes longer (one to 2 hours) than a conventional radiograph.
- More radiation publicity than with conventional radiography.
- Uses ionizing radiation.
- May not reveal each prognosis (e.g. mind tumors, prolapsed spinal disks, and so on.), necessitating the necessity for an MRI.
- All animals should be sedated/anesthetized.
4. MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), like ultrasonography, doesn’t use radiation to supply a picture. Instead, it depends on a mix of magnetic pressure and radio waves.
 Although MRIs are often used to diagnose knee, nerve, and different points in canines, the overwhelming majority are used to look at issues with the mind and spinal wire, particularly if tumors or bleeding are suspected. An MRI is good as a result of it’s notably good for imaging mushy tissue (mind and spinal wire) and it offers extra element than a CT scan. It does this by studying the variations in tissue density to disclose tumors and lesions that CT scans may miss.
Although MRIs are often used to diagnose knee, nerve, and different points in canines, the overwhelming majority are used to look at issues with the mind and spinal wire, particularly if tumors or bleeding are suspected. An MRI is good as a result of it’s notably good for imaging mushy tissue (mind and spinal wire) and it offers extra element than a CT scan. It does this by studying the variations in tissue density to disclose tumors and lesions that CT scans may miss.
Pros
- Often offers a prognosis for a lot of ailments not simply visualized by conventional radiography or ultrasonography, and even CT scan.
- No radiation publicity, making it a really secure imaging modality.
Cons
- Like CT scan, MRI requires referral to a specialty middle, the imaging takes one to 2 hours to finish, and all animals should be sedated/anesthetized.
- More costly in comparison with different modalities (usually $2,500 to $3,500).
- While glorious, no check can reveal each reason behind illness, and even an MRI might not reveal each prognosis.
Echocardiography — important for diagnosing coronary heart illness
Recently, I noticed a canine that had been positioned on three cardiac drugs greater than a yr in the past by one other physician who recognized “coronary heart illness” simply by listening to a coronary heart murmur. No diagnostic testing had been executed, and now the canine had elevated kidney values on blood testing.
I carried out a whole cardiac analysis, together with echocardiography, which confirmed two issues: there was no main coronary heart illness, however the coronary heart was exhibiting unfavorable adjustments because of the improperly prescribed cardiac drugs. The cardiac medication had been additionally negatively affecting the kidneys.
Once we had the proper prognosis and stopped the pointless drugs, the canine improved!
Diagnostic imaging has progressed significantly in veterinary drugs, and it’s thrilling to have all these modalities accessible for our canines and cats. Keep in thoughts that the extra superior the modality, the upper the fee, so it’s smart to think about pet insurance coverage earlier than certainly one of these diagnostic imaging strategies is required. While fundamental radiographs are enough for attending to the basis of most medical circumstances, ultrasonography, CT scans, and MRI scans can assist diagnose downside early on — and that may be lifesaving in lots of instances.