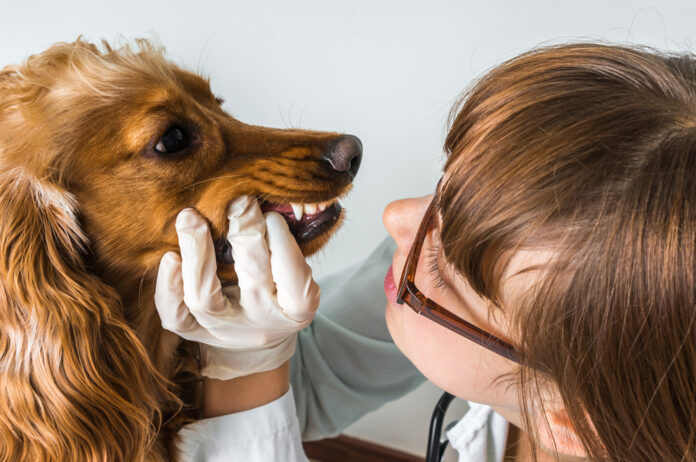
From periodontal illness to crowded tooth, there are numerous explanation why your canine or cat might have a number of tooth extracted. Find out what they’re, and what the process entails.
Periodontal illness is a quite common downside, affecting roughly 70% to 80% of canines and cats beginning at one to 3 years of age. Neglecting or improperly treating the problem can result in additional illness and extra concerned therapy, together with dental extractions. But periodontal illness isn’t the one downside that may necessitate extraction. Find out why your canine or cat may want a number of tooth extracted, and the way it’s achieved.
SIMPLE OR COMPLICATED?
When I consider extractions, I divide them into two classes:
- Simple extractions are generally achieved typically veterinary follow.
- Complicated extractions are sometimes referred to a veterinary dentist with superior coaching and the correct gear to cope with these instances.
Simple extractions in my very own follow fall into two sub-categories:
- Removing retained deciduous (child) tooth
- Removing severely diseased grownup tooth.
RETAINED DECIDUOUS TEETH
Puppies, significantly these of smaller breeds, typically have retained deciduous tooth, mostly the canines (fangs) and incisors (entrance tooth). These are typically straightforward to extract by any veterinarian.
If retained deciduous tooth will not be extracted, they crowd the mouth, trigger irregular dentition, and maintain in tartar and an infection, ensuing within the want for extra frequent dental care. Retained deciduous tooth also can happen in kittens, though I’ve by no means seen this myself.
SEVERELY DISEASED ADULT TEETH
These are additionally pretty easy to take away, and once more happen most frequently in smaller canine breeds. Severely diseased tooth end result from a scarcity of correct residence {and professional} care, and happen when dental tartar eats away on the gum and periodontal ligament holding the tooth in its sockets. Over time (in some small canines it may be a matter of months), the tooth turns into free and requires extraction.
Flag it: Deciduous tooth needs to be eliminated by six months of age, which is when they need to have fallen out on their very own and been changed by grownup tooth.
Flag it: Since the foundation is severely diseased by this time, extraction is sort of straightforward because the tooth is commonly actually falling out of the affected person’s mouth.
I often don’t discover loads of free tooth in cats. Instead, cats sometimes have lesions beneath the gums which might be recognized throughout a periodontal cleansing utilizing dental radiographs. These tooth have severely diseased roots (or in lots of instances no roots, because of extreme illness and destruction), which necessitates extraction. Sometimes throughout a dental cleansing, root publicity or a cavity is detected. These tooth require additional examination and dental radiographs, and can sometimes should be extracted.
EXTRACTION OR ROOT CANAL?
Root canals protect the perform of the tooth. They contain little to no discomfort to your animal, and are much less traumatic than extraction, which entails incising delicate tissue and the elimination of bone. Because a root canal is much less invasive, it permits the animal to eat his regular food plan subsequent day and retains the contour of the higher and decrease jaws (maxilla and mandible.)
Extracting a tooth will be extra invasive and traumatic. The roots of again tooth, the premolars and molars, comprise multiple root. These multi-rooted tooth lengthen deep into the jawbone, and extracting them will take away their chewing perform and lead to bone loss that may weaken the jaw. The excellent news is that almost all canines and cats will do nice after extraction, which is actually preferable to the persistent an infection, ache, and irritation that happens if diseased tooth will not be handled or eliminated.
Flag it: The root of a canine tooth is bigger than the precise crown, and requires extra effort to take away than different tooth.
A follow-up go to for an extraction ought to happen two weeks after the process to verify the incision websites are therapeutic correctly. The canine or cat will likely be positioned on a softened food plan till the recheck examination, after which he can probably return to his earlier food plan.
THE NEED FOR ANALGESIA
Analgesia, or ache prevention and aid, are vital for permitting the canine or cat to be correctly handled with little or no discomfort.
Most docs, together with myself, management dental ache utilizing the next technique:
- Ideally, injectable drugs are first given beneath the animal’s pores and skin previous to the extraction.
- A regional or native nerve block is used to anesthetize a part of the jaw and the related gums and tooth roots. In human sufferers, it’s very straightforward to inform if the nerve is correctly blocked. However, we will’t ask a canine or cat if he stills really feel ache after a block, so we have now to depend on our talent at injecting the anesthetic into the realm of the nerve (if we miss, we nonetheless have the ache aid medicine given previous to and following the process). I can even often instill a drop or two of native anesthesia into the empty tooth socket following the extraction.
- After the process, you’ll take drugs residence (a NSAID, opioid, or related) to manage to your canine or cat for a number of days following the extractions.
Teeth which might be very free and barely nonetheless caught within the socket will doubtless lead to no ache upon extraction as a result of they require little effort to extract and trigger minimal tissue trauma (in some instances, in actual fact, the extraction may make the animal really feel extra snug.) Teeth with diseased roots or which have sustained crown fractures usually tend to trigger ache following extraction as they’re sometimes firmly lodged within the socket and would require extra effort to take away, leading to extra postoperative discomfort if analgesia isn’t used.
Flag it: The diploma of ache concerned in any extraction will depend on the diploma of periodontal illness and the “looseness” of the tooth on the time of extraction.
It’s vital to notice that many sufferers require quite a few tooth extracted because of superior illness. While animal mother and father are sometimes dismayed by the elimination/lack of so many tooth, these extractions truly remedy the animal, cut back irritation and an infection, and cut back the ache of periodontal illness.
What makes tooth extraction mandatory?
- Mobile (free) tooth — brought on by superior periodontal illness and bone loss
- Crowded tooth
- Retained deciduous tooth
- Teeth that intervene with occlusion — the correct “match” with the tooth on the other jaw
- Teeth within the line of a fracture within the mandible or maxilla
- Teeth destroyed by periodontal illness or broken by superior cavities
- Teeth which might be endodontically diseased, corresponding to these containing broken/contaminated pulp, significantly when the animal father or mother chooses to not deal with with a root canal.
What problems can happen with tooth extraction?
While uncommon, problems can happen and embrace the next:
- Hemorrhage — could happen a number of hours post-op if the blood clot retracts or is misplaced by tongue probing
- Oral-nasal fistulas — usually observed pre-op, could take a number of weeks to change into obvious following the elimination of an higher canine tooth
- Gum flap dehiscence — failure of the sutured gums to heal correctly
- Root fracture
- Jaw fracture — extra doubtless in toy or miniature breeds, particularly older canines with extreme illness
- Damage to deep buildings of the jaw — nerves, blood vessels, and so forth.
Setting apart any structural abnormalities in your canine or cat’s mouth, common skilled and at-home dental care will go a great distance in stopping the necessity for extractions. Work along with your veterinarian to ascertain the best dental care routine on your personal companion.
Veterinarian Dr. Shawn Messonnier wrote The Natural Health Bible for Dogs and Cats, The Natural Vet’s Guide to Preventing and Treating Cancer in Dogs, and eight Weeks to a Healthy Dog. He’s the pet care knowledgeable for Martha Stewart Living’s “Dr. Shawn – The Natural Vet” on Sirius Satellite Radio, and creator of Dr. Shawn’s Pet Organics. His follow, Paws & Claws Animal Hospital (petcarenaturally.com), is in Plano, Texas.